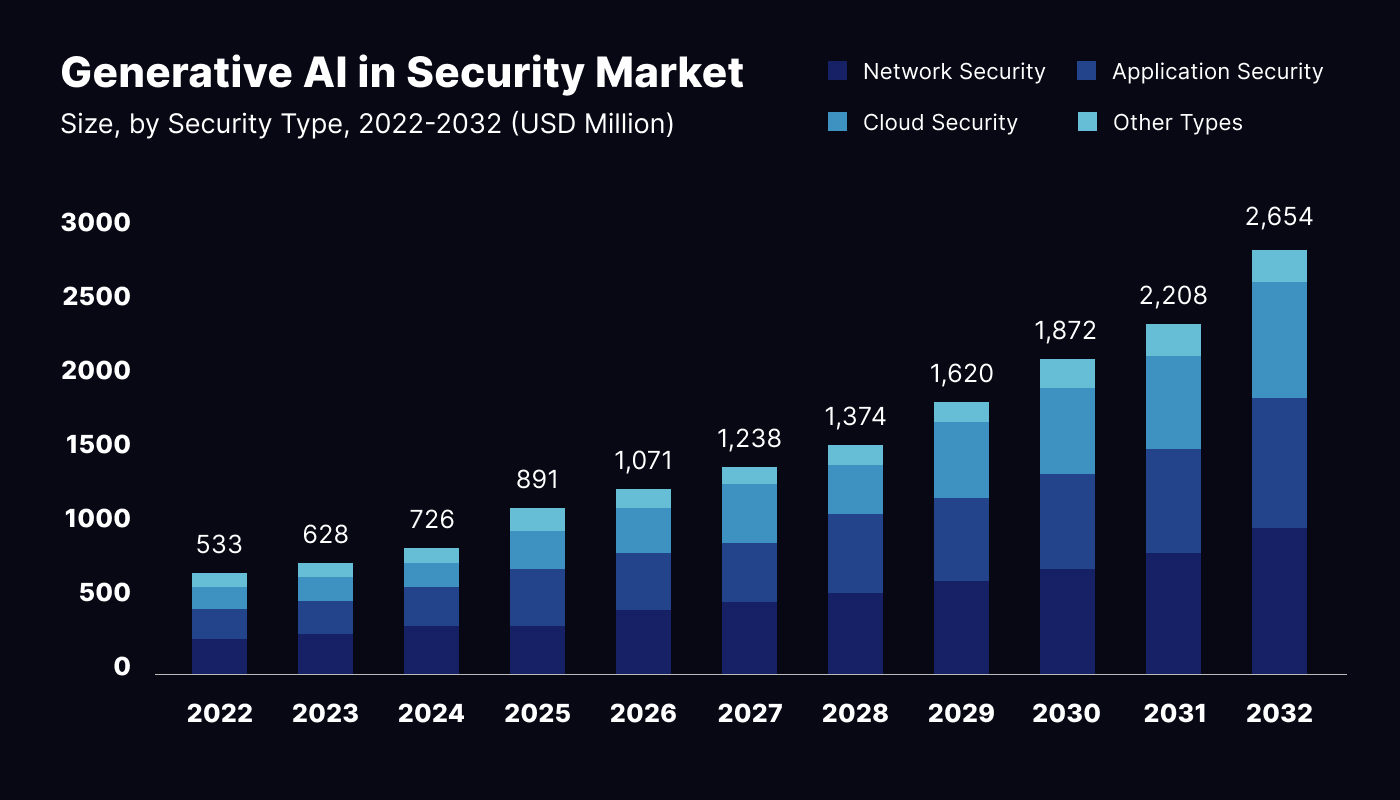
Traditional methods of enforcing cybersecurity are increasingly being outpaced by the sophistication of modern cyber-attacks. Generative AI (GenAI) is a machine learning based technology that is transforming the approach towards cybersecurity by anticipating and mitigating potential threats. GenAI can mimic possible attacks, mask sensitive data with synthetic data, and build an automated approach to incident handling. The Generative AI market for cybersecurity is expected to grow at a rate of 17.9% CAGR to approximately 2.6 million USD by 2032.
Role of Generative AI in Strengthening Cybersecurity
Strengthening threat detection
Traditional methods, like rule-based and signature-based approaches, are effective against known threats but often fall short in identifying new or zero-day attacks. Generative AI addresses this gap by analyzing vast amounts of data, recognizing patterns, and creating models capable of detecting previously unseen threats.
These advanced algorithms can scrutinize network traffic, system logs, and user behavior to identify anomalies and indicators of compromise (IOCs). By learning from historical data, generative AI models detect abnormal patterns and flag potential security breaches in real-time. Moreover, these models continuously adapt and evolve, enhancing their accuracy and effectiveness over time.
Custom LLM over Public LLM for data security
Public large language models (LLMs) offer powerful capabilities, but their widespread use exposes businesses to data leaks and breaches. Unlike public LLMs, which operate in a shared environment with fewer safeguards, custom LLMs incorporate configurable security rules as a fundamental aspect of their design. This customization allows businesses to define and enforce strict security protocols, filtering out sensitive information and ensuring that only essential, safe data is processed.
By adopting custom LLMs, organizations can leverage the benefits of generative AI while maintaining control over their data security. These models provide a secure framework that helps protect intellectual property and sensitive information, reducing the risk of exposure and enhancing overall cybersecurity posture.
Combating Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) represent some of the most sophisticated and damaging cyberattacks, characterized by their stealth and persistence. These attacks often lead to severe consequences, including data breaches, financial losses, and significant reputational damage.
Generative AI models can process a diverse array of data sources—structured and unstructured—including system logs, network traffic, social media feeds, and threat intelligence reports. By synthesizing and integrating this information, generative AI can detect the nuanced patterns and anomalies that signify APT activity, which might elude conventional detection methods. This enables security teams to respond swiftly and proactively to potential threats, mitigating the impact of APTs before they can cause significant harm.
Use Cases of Generative AI in Cybersecurity
Generative AI is revolutionizing cybersecurity through a variety of innovative applications. Here are some key use cases that highlight its transformative impact:
Adaptive threat detection
Generative AI significantly enhances adaptive threat detection by continuously learning from historical data and identifying patterns and anomalies. This allows it to recognize new and evolving threats in real-time, adapting to changing attack tactics and strategies. For example, GenAI can monitor network traffic and detect unusual surges in data requests indicative of potential distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, enabling immediate action to mitigate such threats and alerting security teams.
Predictive analysis
Generative AI excels in predictive analysis by analyzing vast datasets to identify patterns and predict future threats with remarkable accuracy. By studying past attack patterns and vulnerabilities, GenAI can forecast potential future threats, allowing organizations to proactively implement security measures. This real-time analysis provides valuable insights that inform better decision-making and risk mitigation strategies, ensuring a proactive stance against cyber threats.
Malware generation and analysis
Generative AI aids in malware generation and analysis by creating controlled environments for cybersecurity researchers to study malware behavior. By generating artificial malware samples based on known attack vectors, researchers can uncover new insights into malware propagation techniques and evasion tactics. This knowledge helps train cybersecurity teams to recognize and respond to evolving threats effectively.
Enhanced biometrics
Generative AI contributes to enhanced biometrics by generating synthetic yet highly realistic biometric data, such as facial recognition patterns and fingerprint templates. This synthetic data is used to test and refine biometric systems, ensuring accurate distinction between real identities and spoof attempts. Improved biometric authentication enhances security for applications like secure facility access and mobile device unlocking.
Automated security patch generation
Generative AI streamlines the process of identifying, creating, and testing patches for software vulnerabilities. When a critical vulnerability is discovered, GenAI can swiftly analyze it, generate a customized patch, and test it in a controlled environment. This accelerates the deployment of effective patches, reducing the window of vulnerability and ensuring the security of software applications.
Anomaly detection
In anomaly detection, GenAI analyzes massive datasets to discern subtle deviations from established patterns. By continuously monitoring network traffic, system logs, and user behavior, GenAI can promptly identify irregular activities that may signify security threats. For instance, it can detect a sudden spike in outbound data transfers during non-standard hours, triggering immediate alerts and allowing security teams to mitigate potential data breaches.
Phishing detection and prevention
Generative AI enhances phishing detection and prevention by analyzing email content, sender behavior, and patterns associated with phishing attempts. It can identify anomalies in emails, such as suspicious links and grammatical errors, that mimic legitimate sources. By recognizing these patterns, GenAI can alert users to potential phishing attempts, preventing data breaches and financial losses.
Threat simulation and training
Generative AI simulates various cybersecurity threats and attack scenarios in controlled environments to train cybersecurity professionals and incident response teams. These simulations help prepare teams for real-world cyber threats, improving their ability to identify, respond to, and mitigate cyber attacks effectively. This proactive training enhances the overall security posture of organizations.
Why it Is Important for Businesses to Include Generative AI in Security Strategy?
Cybercriminals are constantly changing their modus operandi leveraging state-of-the-art technologies. Generative AI is their latest fascination offering speed, insight, automation, and sophistication to their cybercrime weapons. Typical uses of generative AI by cybercriminals include:
Phishing and social engineering
Generative AI is used to create highly personalized and convincing content that mimics legitimate communications. These tailored messages are designed to trick recipients into divulging sensitive information or downloading malware, making phishing attacks more effective and harder to detect.
Deepfakes
Cybercriminals utilize generative AI to produce realistic audio and video deepfakes. These can impersonate individuals, manipulate public opinion, or conduct sophisticated social engineering attacks, thereby amplifying the impact of their malicious activities.
Malware development
Generative AI aids in creating adaptive and evolving malware that can evade traditional antivirus and malware detection tools. This makes it easier for cybercriminals to deploy malware that is harder to detect and neutralize.
Exploiting vulnerabilities
By analyzing individuals, systems, and software for vulnerabilities, generative AI enables cybercriminals to launch more targeted and effective attacks. This analytical capability allows for the identification of weak points that can be exploited more efficiently.
Automated hacking
Generative AI can automate various aspects of hacking, enabling cybercriminals to execute large-scale attacks that are more complex and difficult to detect. This automation increases the scale and sophistication of their operations, making them more challenging to counter.
Bypassing security measures
AI models can be trained to mimic user behavior or generate inputs that bypass security systems such as biometrics, CAPTCHAs, and other AI-based defenses. This ability to trick security measures makes it easier for cybercriminals to infiltrate protected systems.
The cybersecurity landscape is very competitive with both the cybercriminals and security professionals constantly upgrading their strategy, techniques, and operational tools. This entails businesses maintaining their security posture leveraging technologies like Generative AI.
Conclusion
As the cybersecurity landscape evolves, we will witness a wider adoption of Generative AI to improve security posture. Sophisticated models will be developed that can anticipate threats and mitigate them in a proactive manner. Automation through GenAI will enhance operational efficiency and significantly reduce the likelihood of human error. Cybersecurity training will highly utilize GenAI generated synthetic scenarios to build deep technical expertise and enhance the ability of critical thinking and swift reaction. There will be a trend of creating custom LLMs in order to keep proprietary data confidential. New regulations will be issued for public LLMs in order to maintain data security and confidentiality. Overall, integrating GenAI will transform how organizations today practice cybersecurity.
