The AWS re:Invent 2023 was kicked off by Peter DeSantis in a keynote session at the heart of which lies a pivotal focus on advancing serverless capabilities within the cloud. The keynote session delved into the groundbreaking innovations that push the boundaries of serverless computing.
This year’s announcements bring a trio of game-changing capabilities, particularly in the realm of serverless databases.
The introduction of Amazon Aurora Limitless Database stands out, offering automatic scalability beyond previous constraints, revolutionizing application scaling.
Complemented by enhancements in Amazon ElastiCache and Amazon Redshift Serverless databases, these unveilings promise heightened workload performance and cost optimization. This year’s re:Invent sets a new benchmark in simplifying serverless solutions for developers and businesses alike.
Amazon Aurora Limitless Database
Enterprises today create and store petabytes of information from multiple sources, and require an end-to-end strategy to analyze and manage it at scale. AWS offers a variety of cloud-based big data services to aid in these strategies. Currently, tons of customers use Amazon Aurora Serverless for its ability to adjust capacity up and down to support hundreds of thousands of transactions.
However, for some customers, this scale is simply not enough. There are certain applications, such as financial transaction processing and gaming, that need to support hundreds of millions of users globally. Most organizations attempt to do this by scaling horizontally and distributing the workload across multiple smaller database instances.
This process is known as sharding and requires the development of customized software that can shunt requests to the best instance and make changes across multiple instances. Database activity must also be monitored in real time, and it creates an enormous overhead for customers running their own data platforms.
The newly launched Aurora Limitless Database solves this issue by enabling users to scale the write capacity of their Aurora database beyond the write capacity of a single server.
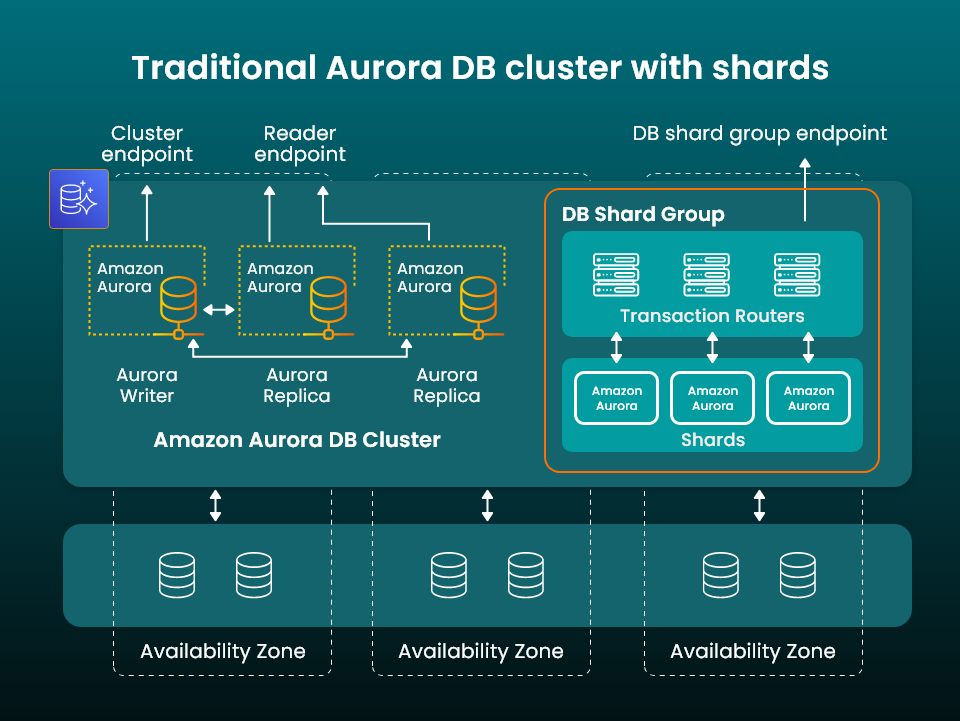
It does this partly through sharding, enabling users to create a Database Shard Group containing shards that each store a subset of the data stored in a database. They’ve also taken into account transactions, and provide transactional consistency across all shards in the database. The best part is that it removes the burden of managing a sharded solution from the customer, while providing the benefits of parallelization.
Customers no longer need to create customized software to route requests to the appropriate database instances. Instead, the platform does everything automatically, while scaling horizontally or vertically according to the needs of their applications. For engineering teams, maintenance operations are simplified, as any changes can be made just once and applied to multiple database instances, instead of implementing each one manually.
Amazon ElastiCache Serverless
Amazon ElastiCache is used by applications to store their most frequently accessed data and enhance their performance and scale. However, traditionally caches are not serverless and require a ton of resource planning.
Some companies want to get started early without getting involved in the infrastructure management and resource planning, and this is what the new Amazon ElastiCache Serverless feature addresses. It’s a serverless option of ElastiCache that enables the customer to launch a Redis or Memcached caching solution without having to provision, manage, scale, or monitor a fleet of nodes.
It is a sharded caching solution where the entire setup process is fully automated, and the service can automatically replicate data across multiple availability zones with up to 99.99% availability for any workload.
AI Driven Optimization for Amazon Redshift Serverless
The Amazon Redshift service is a great solution for proactively provisioning resources and scale database capacity depending on the query volume. This mechanism works fine with uniform queries but upon encountering large complex queries the system may slow down and also impact other smaller queries.
The Amazon Redshift Serverless takes an unique approach to provision resources on the fly leveraging the power of AI. The next-generation AI-driven scaling and optimization solution takes into account query structure, data size, and other metrics to anticipate the query load. Resources are ramped up or scaled down accordingly to ensure customers can achieve their specified price/performance targets.
For example, at times of low demand Redshift can automatically reduce the database capacity and ramp up if encountered with a complex query. Then again during high demand hours it can automatically boost its capacity while accounting a cost-benefit analysis.
Conclusion
Data has a very dynamic nature and on the fly infrastructure provisioning is what serves it best in terms of cost and resource optimization. The very nature of serverless architecture fits into this characteristic of data and enables customers to scale to millions of transactions per second, swiftly step up capacity, and dynamically adapt to changing workload patterns. The three latest innovations to serverless computing from AWS opens up immense opportunities for businesses managing their cloud platform.
