The use of ML and other cognitive disciplines for medical diagnosis is an important use of AI in healthcare. AI can assist doctors and other healthcare professionals in providing more precise diagnoses and treatment recommendations by using patient data and other information. By analyzing large data to create better preventive care suggestions for patients, AI can also assist in making healthcare more proactive and predictive.
AI can help healthcare professionals including doctors, nurses, and others with their regular tasks. AI in healthcare can improve patient outcomes overall, improve preventative care and quality of life, and create more precise diagnosis and treatment strategies. By examining data from the public sector, the healthcare industry, and other sources, AI can help forecast and monitor the development of contagious diseases. As a result, AI has the potential to be a key component of the global public health effort in the fight against pandemics and epidemics.
“By augmenting human performance, AI has the potential to markedly improve productivity, efficiency, workflow, accuracy and speed, both for [physicians] and for patients… What I’m most excited about is using the future to bring back the past: to restore the care in healthcare.”
– Eric Topol, MD, director and founder of Scripps Research Translational Institute
Breakthroughs for AI in Healthcare
Embedded ML in Asthma Inhalers
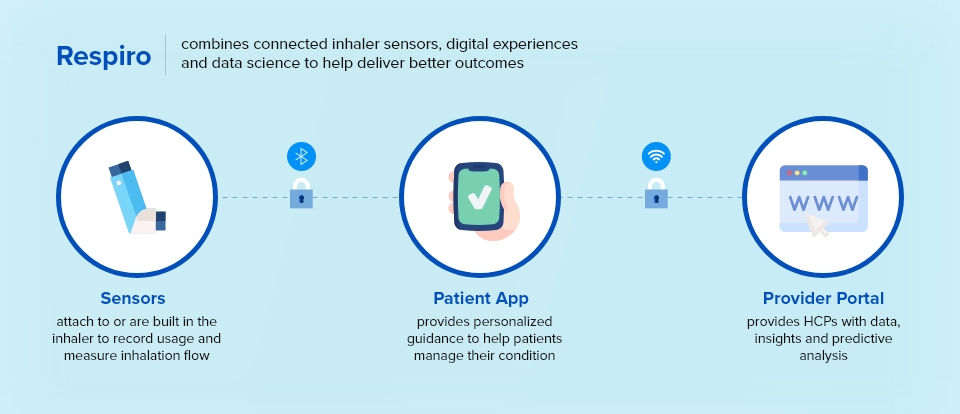
Respiro is the first commercial inhaler in the world that accurately tracks inhalation methods, frequency, and patient management while delivering detailed information to the patient and doctor. Respiro combines connected inhaler sensors, digital experiences, and data science to help deliver better outcomes.
Heart Attack-Detecting AI

By identifying urgent illnesses in real time, artificial intelligence (AI) from the Danish start-up Corti assists emergency dispatch employees in making decisions that could save lives. Using the words, sounds, and breathing patterns from the call, dispatchers can be guided to pose the pertinent inquiries that could hasten the administration of crucial CPR.
On the dispatcher’s desk, the Corti Orb is a user-friendly, fashionable plug-and-play gadget that listens to calls while using sophisticated machine learning (ML) models to identify life-threatening conditions in real-time. According to studies on the effectiveness of the Orb, trained dispatchers correctly identified cardiac arrest in 73 percent of cases, but the AI device correctly identified cardiac arrest in 95 percent of cases with a significantly shorter time to the identification.
Google Creates AI that Detects Lung Cancer Better than Doctors

Recently, Google researchers collaborated with Northwestern Medicine to develop an AI system that can identify lung cancer with more accuracy than radiologists. This system, which analyses computed tomography (CT) scans to forecast one’s likelihood of getting the disease, was trained using a deep-learning algorithm. The study’s lead author is Daniel Tse, a product manager at Google Brain. It was published on May 20 in the journal Nature Medicine.
Discovering Causes of Autism in Uncharted DNA

A study team has recently discovered unique genetic abnormalities linked to autism in non-coding areas of DNA using artificial intelligence (AI). These “junk” portions of the genome, which may not alter what certain genes produce but rather how much of it they make, were examined by the researchers using deep learning.
The genomes of 1,790 families, where one child has autism and the rest of the family does not, were subjected to this deep learning AI technique. The researchers were able to hypothetically isolate mutations that were particular to autism by limiting their investigation to such cases of autism.
AI in Healthcare in Stats
- The global artificial intelligence in healthcare market size was valued at USD 10.4 billion in 2021 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.4% from 2022 to 2030.
- 41% of Americans prefer AI doctors for primary consultation.
- 62% of providers believe that AI is most beneficial to the healthcare industry
Applications of AI in Healthcare
Support in Clinical Decisions

It goes without saying that while diagnosing patients, medical practitioners must take into account every significant piece of information. This necessitates searching through a variety of intricate, unstructured notes that are stored in medical records. The patient’s life could be in danger if there is even a single crucial fact that is missed from the record.
Natural language processing (NLP) makes it easier for medical professionals to extract all pertinent data from patient reports.
Large data sets can be stored and processed by artificial intelligence, which can then be used to create knowledge databases, make it easier to examine and prescribe treatments specifically for each patient, and otherwise improve clinical decision-making.
By analyzing unstructured notes, this technology can be used by doctors to help identify risk factors. An intriguing illustration of this is IBM’s Watson, which uses AI to forecast heart failure.
Robotic Surgery

Surgery has been changed in terms of its speed and depth while creating delicate incisions thanks to AI and collaboration robots. Robots don’t get sleepy, thus the problem of being tired in the middle of time-consuming and important procedures is eliminated.
AI systems are capable of using information from previous procedures to create novel surgical techniques. These devices’ accuracy lessens the chance of tremors and any unintentional or accidental motions during operations.
Vicarious Surgical, which combines virtual reality with AI-enabled robots so surgeons can perform minimally invasive operations, and Heartlander, a tiny mobile robot developed by the robotics department at Carnegie Mellon University, are two examples of robots created for surgeries. Heartlander was created to facilitate therapy on the heart.
Virtual nursing assistants

Virtual nursing assistants are made possible by AI systems, and they are capable of a variety of duties, including interacting with patients and directing them to the most suitable care setting. These virtual nurses can evaluate patients, answer to questions, and offer immediate remedies. They are accessible around the clock.
In order to prevent any needless hospital trips, a lot of AI-powered applications of virtual nursing assistants already offer more frequent interactions between patients and care providers between office visits. Even wellness checkups can be facilitated by the world’s first virtual nurse assistant, Care Angel, using voice and AI.
Diagnosis of Chronic Diseases

AI has the potential to outperform human physicians and aid them in more quickly and accurately detecting, predicting, and diagnosing illnesses. Similarly, AI systems have shown to be cost-effective in diagnosing diabetic retinopathy while also being accurate and precise at specialty-level diagnosis.
For example, PathAI is creating machine learning technologies to help pathologists identify diseases more accurately. The company’s current objectives include lowering cancer diagnosis inaccuracy and creating strategies for personalized medical care.
An AI-based symptom and cure checker called Buoy Health uses algorithms to identify and treat illnesses. The process goes as follows: a chatbot asks a patient about their symptoms and health concerns, then, after making a diagnosis, directs the patient to the appropriate care.
Some businesses are increasing diagnostic accuracy by 90% by analyzing medical imaging results using AI. While some systems, like Ultronics’ EchoGo, can analyze over 8,000 data points from each echocardiography image, others, like Zebra Medical Vision’s Profound software, are better at spotting breast cancer, fatty liver, aneurysms, and emphysema symptoms. Instead, the AI2 Incubator and Fujifilm SonoSite used portable ultrasound machines to deploy deep learning models. In order to use ultrasound images more affordably and without putting patients at risk, they are now created more effectively.
Know about how we created a custom-trained ML model to detect Covid, Pneumonia, and COPD Diseases from chest XRay Scans
Reducing the burden of using EHRs

EHRs have been a crucial part of the healthcare sector’s transition to digitization, but this change has also brought up a number of problems, including cognitive overload, excessive documentation, and user burnout.
AI is now being used by EHR developers to build more user-friendly interfaces and automate a few of the repetitive tasks that take up a lot of the users’ time.
Although dictation and voice recognition are improving the clinical recording process, natural language processing (NLP) methods might not be as effective. AI can help process typical email requests, like requests for medicine refills, and produce notifications as a result. It can also aid in prioritizing chores that require the clinician’s attention, making it simpler for the users to work with their to-do lists.
Enhance Primary Care and Triage through Chatbots

At the first sign of a threat or medical condition, people have a tendency to schedule appointments with their general practitioner, even when it may just be a false alarm or something that can be resolved with self-care.
Artificial intelligence helps to facilitate the automation of primary care, freeing up doctors to focus on more urgent and serious patients.
Medical chatbots, an AI-powered service with clever algorithms that give users fast answers to all of their health-related questions and worries while also advising them on how to cope with any potential problems, can help people save money on unnecessary trips to the doctor.
These chatbots can manage numerous patients at once and are accessible around the clock.
Large-Scale AI-Based Insights

Data-driven insights are essential for health care organizations and governments to develop new health policies that may be beneficial to the population at large. KenSci’s risk prediction platform aggregates data from admission, discharge, and transfer systems, claims, and EHRs to provide insights into chronic diseases such as COPD, Chronic Heart Failure, and diabetes.
This platform can help people reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes by using wearable devices and lifestyle changes, and by identifying where expensive and variable drugs are being purchased. Microsoft is working with national governments to identify which COPD patients are getting worse and who may need a higher dose of medication. The use of oral acetaminophen to treat pain has been proven to be more effective and less costly than other treatment methods.
Threats of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
According to a Brookings Institution paper, there are a number of concerns related to AI in healthcare that need to be taken into consideration. The following are a few of the threats listed in the Institution’s report:
Errors and Injuries
One of the major dangers of using AI in healthcare is that it might occasionally make mistakes. For example, it might recommend an incorrect prescription to a patient or misidentify a tumor in a radiology scan, which could endanger the patient’s life.
There are at least two potential differences between human and AI errors. While mistakes can undoubtedly be made by human medical practitioners as well, this is important because an underlying mistake or mistake in an AI system could cause harm to thousands of patients.
Issues with Data
The need for enormous amounts of data from numerous sources, such as pharmacy records, electronic health records, insurance claim records, etc., for training AI systems is another hazard these systems pose.
The data becomes confusing and harder to understand since it is fragmented and patients frequently change insurance plans or providers. As a result, the risk of inaccuracy and the expense of data gathering rise.
Privacy Concerns
The capacity of AI to predict patients’ private information, even if the patient has never provided it, is another area where the use of AI systems poses this concern.
For example, Parkinson’s disease could be identified by an AI system based on the trembling of a computer mouse, even if the patient hasn’t disclosed the condition to anybody else. The patient may view this as a breach of privacy.
Bias and Inequality
Since AI systems learn and are taught using the data that is available, they can also absorb the biases of that data. For instance, if the data used in AI is primarily gathered in academic medical institutions, the systems under development will be less aware of, and as a result, will treat patients from groups that do not generally visit academic medical centers less effectively.
Conclusion
The healthcare sector can benefit from artificial intelligence tools by providing quicker service, more precise diagnosis, and data analytics for spotting trends or any genetic information that would predispose someone to a specific ailment.
We live in a time when even a few minutes can mean the difference between life and death, and in this context, artificial intelligence and machine learning have the potential to revolutionize healthcare for everyone as well.
Chronic diseases and cancers can be diagnosed more accurately and efficiently with new AI-based technologies, which can also help researchers better assess risks. The healthcare industry is complex and has a number of constraints that can be overcome with the help of artificial intelligence.
The future of healthcare is working together with health technology, and healthcare workers have to accept emerging healthcare tech to stay relevant in the years to come.
Talk to us at gleecus.com/contact-us