The post-pandemic market has seen an aggressive adoption of the cloud in retail business ecosystem. From tracking supply chains to bringing all customers under one stream of service through omnichannel marketing strategies, cloud computing has added value to every service component in the retail industry.
Cloud in retail: Emerging facts
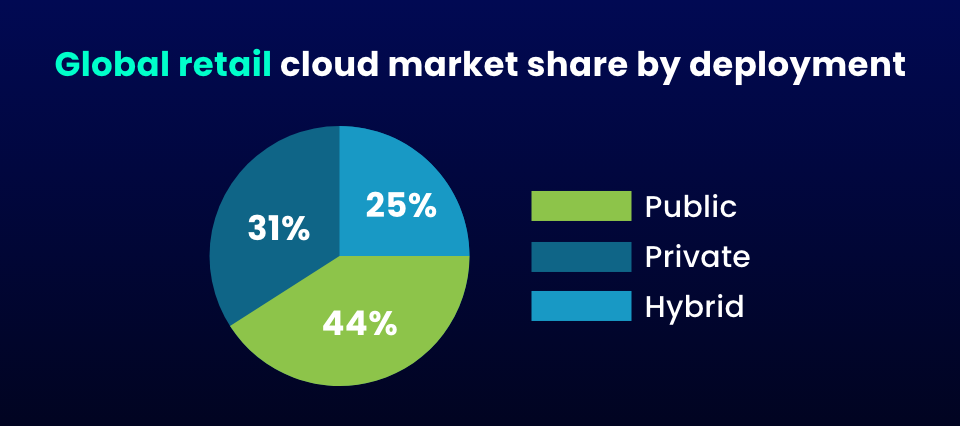
In recent years, the retail sector has seen a shift in cloud adoption. Many retailers have begun to adopt hybrid cloud solutions, which combine public and private clouds. While sensitive data is stored in private clouds, public clouds are preferred to deal with less sensitive data.
A study by Fortune Business Insights found that the global retail cloud market was worth $11.89 billion in 2018. It is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.3% from 2019 to 2026.
The growing adoption of IoT, AI, and ML in retail requires agile data management and scalable storage. This is also a contributing factor to the growing popularity of cloud based solutions.
Efficient Inventory Management
Large retail companies with multiple stores in different locations often struggle to track inventory in real time. Cloud computing provides real-time data and analytics platforms to overcome this challenge. Retailers no longer need to manually synchronize inventory data between stores. Instead, they can access real-time stock availability data from anywhere.
Retailers also can build predictive and prescriptive inventory forecasting models, which can significantly reduce stock shortages. Overall, cloud computing can help retailers improve inventory management and reduce stock shortages. This can lead to increased sales, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced costs.
Analytics Driven Price and Margin
Pricing drives purchase especially when customers are aware of a retail competitors’ prices. Existing manual process of analyzing sales history at a granular level and coming up with a re-pricing strategy is time taking. Additionally, data is often siloed across different channels, making it difficult and time-consuming to derive insights.
Retail Cloud Computing helps retailers address these challenges by ingesting and preparing data from multiple sources Additionally, the cloud makes it possible to seamlessly combine data and gain insights through machine learning and business analytics.
It is important for decision-makers to carefully evaluate cloud providers. When selecting a cloud provider, retailers should consider the following factors:
- The ability to quickly build a data platform
- The availability of intrinsic analytics
- The ability to provide best-in-class machine learning capabilities
Here are some additional benefits of using Retail Cloud Computing for pricing strategy:
- Real-time pricing: The cloud can help retailers to set prices in real time, based on factors such as demand, inventory levels, and competitor pricing. This can help retailers to stay competitive and maximize profits.
- Targeted pricing: The cloud can help retailers to target their pricing to specific customer segments. This can be done by using machine learning to segment customers based on their demographics, purchase history, and other factors.
- Personalized pricing: The cloud can help retailers to personalize their pricing to individual customers. This can be done by using machine learning to predict how much each customer is willing to pay for a product.
By using Retail Cloud Computing, retailers can gain a competitive advantage by optimizing their pricing strategy.
Omnichannel Order Fulfillment
Growth of eCommerce has led to the rise in demand for retail cross-channel fulfillment. Customers are adapting to the BORIS (Buy online return in store) and BOPIS (Buy online pick up in store) style of shopping. As a result retailers need to gear up for a perfect omnichannel strategy that involves handling a significant amount of data. Cloud computing can help retailers to meet the challenges of omnichannel order fulfillment. Here are some of the ways in which cloud computing can help:
- Real-time inventory visibility: Cloud-based inventory management systems can provide retailers with real-time visibility into inventory levels across all channels. This information can be used to ensure that orders are fulfilled quickly and accurately, regardless of where the order was placed.
- Automated order management system: Cloud-based OMS (Order management system) keeps track of inventory across all channels. They can automate route planning and reduce shipping cost by shipping from the right node at the right cost. Smart routing increases efficiency, reduces human error, and reduces time for customer service. It can also free up employees to focus on other tasks, and reduce expenses.
- Flexible scalability: Cloud-based systems can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing demand. This can help retailers to avoid overspending on capacity during periods of low demand, and it can also help them to meet spikes in demand during peak periods, such as the holiday season.
- Improved customer experience: Cloud computing can help retailers to improve the customer experience by providing them with a more seamless shopping experience. For example, customers can place orders online and pick them up in-store, or they can order online and have their orders shipped to their home or office.
Overall, cloud computing can be a valuable tool for retailers who are looking to improve their omnichannel order fulfillment capabilities. By using cloud computing, retailers can improve efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Data Security
Cloud computing is a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes. It can help businesses to store and manage large amounts of data, such as sales data, stock/inventory data, and customer data. Cloud comes with a lot of advanced features to protect data like:
- Advanced firewalls: Firewalls protect data from unauthorized access.
- Data encryption: Data encryption masks data and is the second layer of protection if a firewall is breached.
- Event logging: Event logging helps to track suspicious activity and identify potential security breaches.
Enhanced Profitability
Cloud computing is enhancing profitability of retailers through cost-effective solutions in a number of ways.
- Cost savings: Cloud computing can help retailers save money on IT infrastructure, licensing, maintenance, and support costs. This is because retailers do not need to purchase and maintain their own hardware and software. Instead, they can access these resources on demand from a cloud provider.
- Increased agility: Seamless scaling of resources allows retailers to increase their capacity when there is an influx of customers. Retailers can also save cost by limiting the resources in off season.
- Improved customer service: Cloud-based inventory management systems can help retailers track inventory levels in real time and identify stock shortages. This can help them to improve customer service and avoid lost sales.
- Enhanced decision-making: Cloud computing can help retailers enhance decision-making by providing them with access to real-time data and analytics. This data can be used to identify trends, optimize operations, and improve profitability.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is still a relatively new technology, but it is rapidly gaining momentum in the retail industry. As cloud computing technology continues to evolve, it is likely to offer even more benefits for retailers. In the future, cloud computing could play a major role in helping retailers to improve their operations, increase customer satisfaction, and achieve their business goals.
