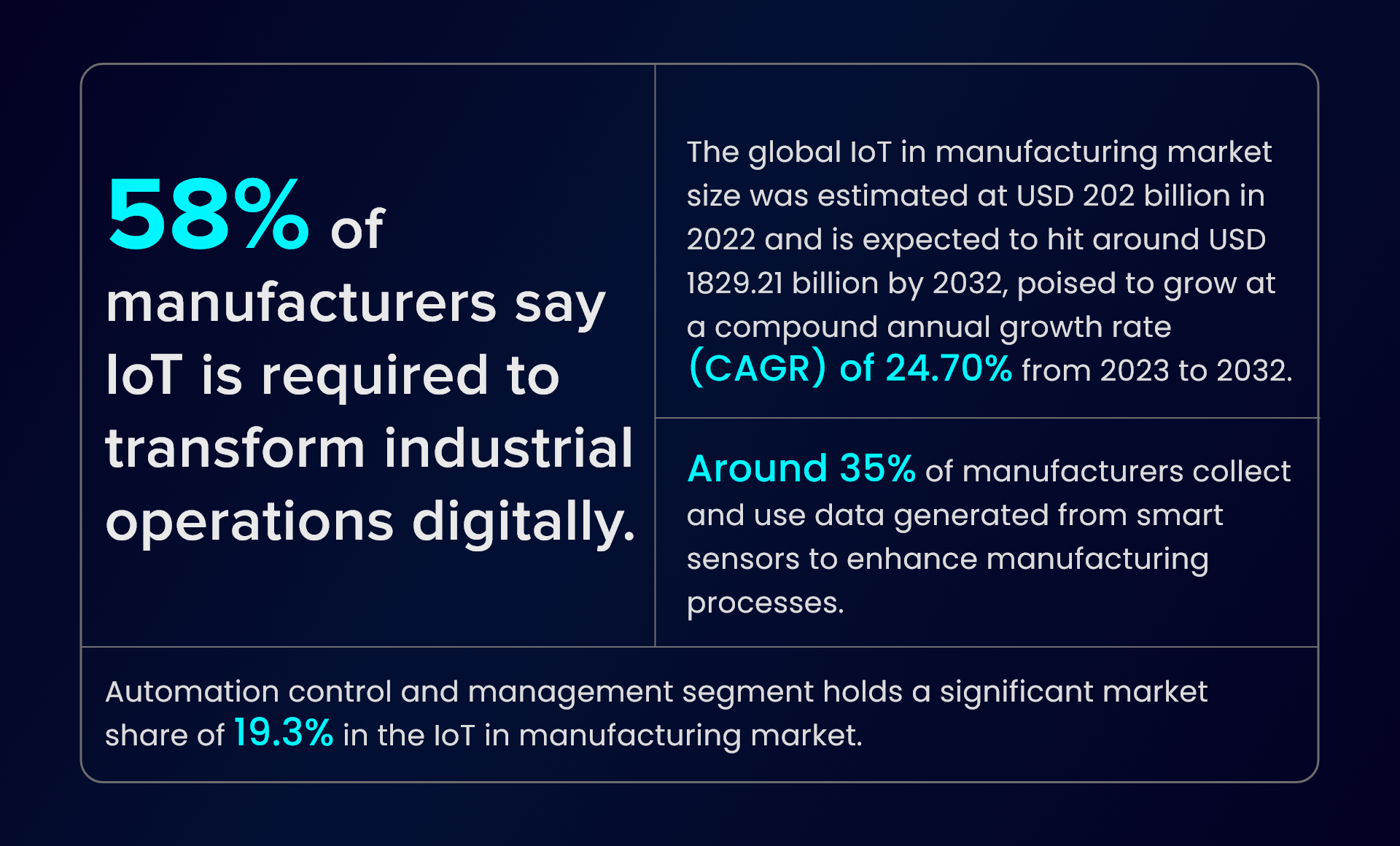
In the transformative era of Industry 4.0, the Internet of Things (IoT) stands as a crucial catalyst reshaping the manufacturing industry. The implementation of IoT in manufacturing has facilitated the adoption of digital technologies like cloud computing and Big Data, creating a seamless integration that enhances operational efficiency and productivity. IoT has revolutionized data utilization, communication, and operational practices across industries. This evolution has given rise to the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), marking a significant shift in manufacturing operations. With a persistent drive to enhance productivity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, the manufacturing sector increasingly relies on IoT as a promising solution to address these ongoing challenges.
How IoT in Manufacturing Is Bringing Transformations
The Internet of Things (IoT) comprises a network of sensor-equipped physical objects that gather and share data, enabling connectivity among different machines, systems, and devices. This connectivity empowers manufacturers to minimize downtime and enhance production processes. Moreover, leveraging the wealth of information and capabilities available, IoT in manufacturing facilitates the development of new revenue streams and innovative business models within the manufacturing sector. Here are several ways in which IoT benefits the manufacturing industry.
Predictive maintenance
IoT sensors monitor equipment health in real-time, allowing manufacturers to predict and address potential issues before they cause breakdowns. This helps to eliminate unplanned, reduce planned downtime, lower maintenance costs, and prevent supply chain disruption.
Improved customer satisfaction
IoT-enabled products can provide real-time data on performance and usage. Manufacturers can proactively track customer feedback to address customer concerns and offer remote diagnostics and support.
Supply chain connectivity and asset management
IoT-connected devices track the location and status of materials and products across the supply chain, enabling real-time visibility, improved inventory management, and optimized logistics.
Higher operational intelligence
Data collected from connected devices provides insights into production processes, machine performance, and resource utilization, allowing for data-driven decision-making, process optimization, AI integration, and improved overall efficiency.
Improved production planning
Real-time data on inventory levels, demand fluctuations, and equipment performance enables manufacturers to adjust production plans dynamically, optimize resource allocation, and meet market demands efficiently.
Robust security
Implementing robust security measures for IoT devices and data is crucial. This includes secure communication protocols, access controls, and data encryption to protect against cyber threats and ensure reliable operations.
How The Current IT Landscape Helps with IoT Adoption in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, the applications of IT and OT (Operational Technology – machinery and essential infrastructure) differ significantly. While small devices like sensors and monitoring systems have traditionally collected data related to OT for reactive responses, IT has leveraged data from modern digital technologies (like cloud computing, mobile applications, BI tools, and customer responses) for proactive analysis and planning.
However, in the era of IoT, this disparate OT data can be combined, and centrally integrated over IT infrastructure like cloud platforms for greater business use. IoT in manufacturing means integration of machines with sensors and actuators through Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), connected via a cloud-native application like Manufacturing Execution System (MES) leveraging services like AWS IoT Core. This integration enables secure data sharing within an enterprise through the intranet and the internet. This bi-directional data exchange allows for communication between the machinery and shopfloor managers, as well as the products, which can be equipped with sensors to create smart products that enhance customer experiences.
Additionally, IoT sensors, cameras, gauges, and monitoring applications can be integrated to the machinery to gather data. Maintenance teams can utilize this data to track the manufacturing process remotely, eliminating the need to be physically present on the shop floor. These intelligent devices can also issue alerts over monitoring dashboards regarding various disruptions such as connectivity problems, potential machine failures, or changes in equipment behavior caused by fluctuations in pressure, temperature, humidity, vacuum levels, or vibration. This proactive approach ensures timely maintenance interventions with minimal or zero downtime, resulting in substantial cost savings amounting to millions of dollars.
Lower cost of ownership
Cloud-based platforms and solutions like ThingWorx, GE Predix, AWS IoT Core, and Microsoft Azure IoT Hub offer subscription-based models that have significantly reduced the cost of ownership for IoT solutions. This cost reduction allows small and medium businesses to incorporate IoT into their manufacturing processes, a capability that was previously exclusive to large manufacturing enterprises. By implementing IoT, manufacturing businesses can enhance their quality control processes, optimize production efficiency, and create new revenue streams through innovative business models.
Improved quality
The increasing adoption of IoT on the consumer side has led to a decrease in the cost of industrial-standard sensors, controllers, and networks. This cost reduction has made it more accessible for businesses to integrate IoT-connected sensors across various manufacturing equipment, including areas that have not previously seen significant automation investments, such as balance-of-plant equipment and supply chain logistics. The data collected by these sensors can be utilized by factory floor workers, plant managers, software systems, and various aspects of the supply chain to fine-tune machine configurations and subassembly lines. This improvement in product quality ultimately strengthens customer loyalty and enhances the relationships between manufacturing, sales, and distribution.
Enhance the shop floor
IoT-enabled sensors and devices integrated into the assembly line, connected to the Manufacturing Execution System (MES), provide real-time data on the machines’ state, production efficiency, production line status, and dashboards. This data, accessible through the cloud from any geographic location, empowers leaders, from the Chief Experience Officer to shop-floor supervisors, to make informed decisions at the right time. It also fosters collaboration between manufacturers, the supply chain, and suppliers. The data can further streamline the manufacturing ecosystem by connecting all devices on an IP network, enabling manufacturers to optimize and automate shop floors across the globe. With minimal personnel required to manage production systems, these automated processes can trigger raw material PO, changeover to produce different products, and streamline manufacturing processes. In the near future, machines will communicate with and monitor other machines, leading to an extremely automated manufacturing environment.
Fine-tune maintenance
IoT-enabled devices can revolutionize the manufacturing sector by providing continuous monitoring of machinery and predicting maintenance based on historical data. Machine learning algorithms can detect abnormalities in production parameters such as vibrations, noise, temperature, humidity, vacuum, and pressure, and quickly send alerts to monitoring applications. This proactive approach helps to increase machinery uptime and enhance product quality. By addressing untimely machine breakdowns and parametric changes, manufacturers can ensure that their machinery operates at peak efficiency, ultimately improving product quality and customer satisfaction.
Boost energy efficiency
Energy plays a crucial role in manufacturing operations, significantly impacting costs. Effective energy management can lead to substantial savings depending on the specific manufacturing setup. Many manufacturing companies overlook the potential of IoT-based devices to optimize energy usage across their machinery, facilities, and supply chains. By focusing on optimizing key systems, such as integrating motion-sensor-based lighting, adjusting temperature controls based on weather conditions and shift schedules, and centralizing control of lighting and HVAC systems, manufacturers can reduce expenses and enhance energy efficiency to achieve greater savings.
Optimize the supply chain
The data generated by IoT devices empowers manufacturers to develop predictive models using machine learning for raw material needs across various products and enhance their understanding of the delivery challenges faced by supply chain partners. By analyzing parameters like dependencies, material usage, supplier inputs, and manufacturing cycle times, suppliers and partners in the supply chain can collaborate towards achieving just-in-time manufacturing. This data also facilitates tracking of inventory levels, locations, production rates, and product deliveries, enabling optimization of inventory management and capital costs.
Challenges of Adopting IoT in Manufacturing
Security
Ensuring security can present a challenge during the integration of IoT within the manufacturing environment. While devices within the realm of IT benefit from encryption and robust physical and network security measures, those categorized under OT lack a comparable level of security infrastructure. To enhance security and prevent potential incidents like machinery breakdowns resulting from malware downloaded through insecure remote access, OT systems must incorporate user-level authentication and identity systems. Most public cloud service providers like AWS, Azure provide an extra layer of security through a number of authentication tools and services.
Software and protocols
IoT encompasses a combination of IT and OT systems, each with distinct datasets. Analytical systems must be capable of comprehending various data sets, including information from PLC logic and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines, to develop models that can be translated into actionable insights for the manufacturing ecosystem. This includes monitoring and managing instruments, safety sensors, and the Manufacturing Execution System (MES). To facilitate informed decision-making, analytical systems require appropriate software for creating correlated statistical models. Simplifying the handling of multiple protocols is essential to enhance interoperability.
Conclusion
IoT technologies are transforming manufacturing operations and driving the evolution of the next era in manufacturing with billions of IoT-enabled sensors, gauges, and cameras producing vast amounts of data. To fully realize the benefits of IoT in manufacturing, manufacturers must be able to embrace and leverage the IoT-derived insights to enhance manufacturing processes, product quality, and operational efficiency, all while prioritizing timely maintenance. Collaborating with IoT solutions companies can help manufacturers overcome the challenges and successfully implement IoT technologies to improve their operations.
